Tropical Rainforest Plants Adaptations To Environment

Tropical Rainforest Plant Adaptations.
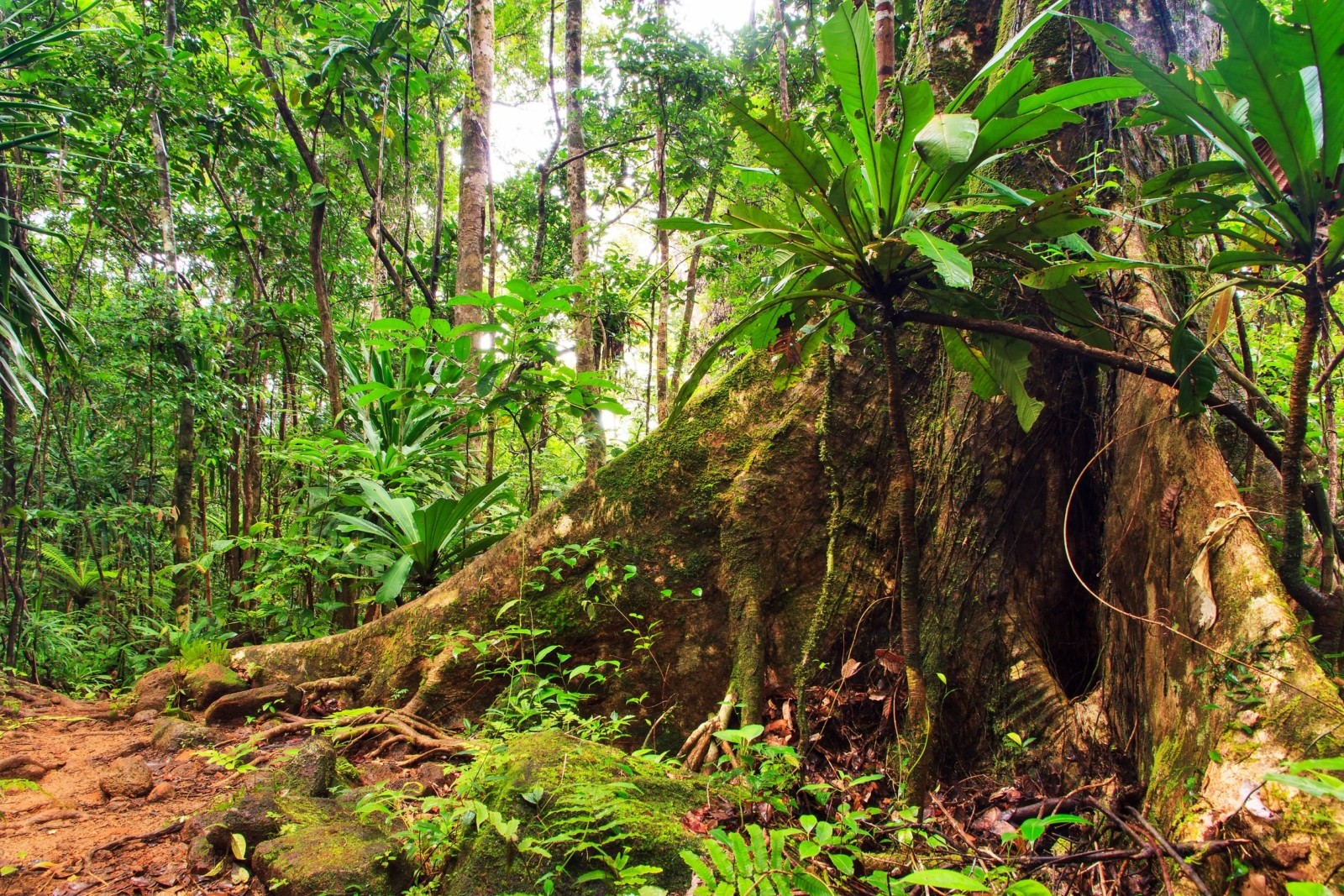
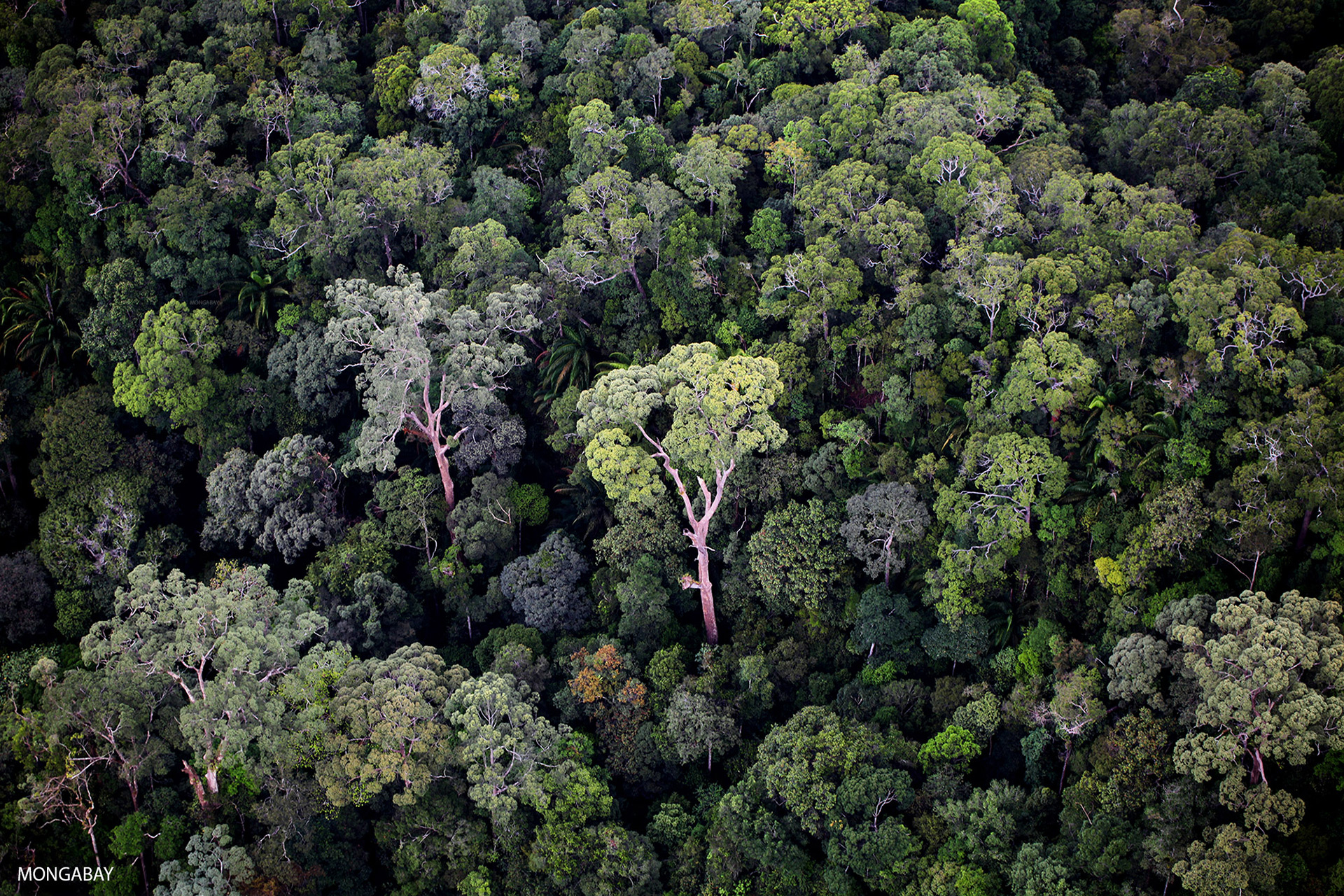
Tropical rainforest plants adaptations to environment. Tropical rainforest flora have to adapt to an environment that is always hot and wet. Plants and animals living in the Tropical Rainforest must be able to adapt to the year round humidity and constant warm humid and wet weather. In the rainforest it rains anywhere from 50-260 inches per year which means that the trees.
Some rainforest trees have special characteristics which are signs of adaptation to their environment. TropicalRainforestPlants tropical rainforest animals. A rain forest is an environment that gets a lot of rain.
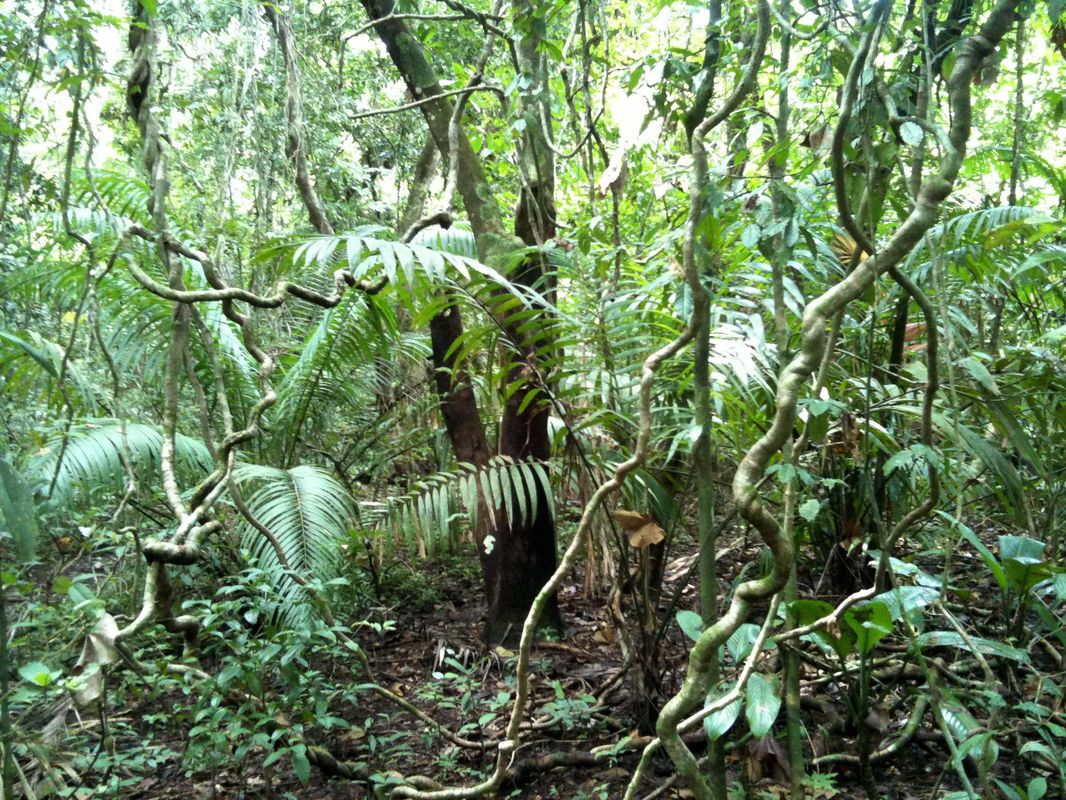
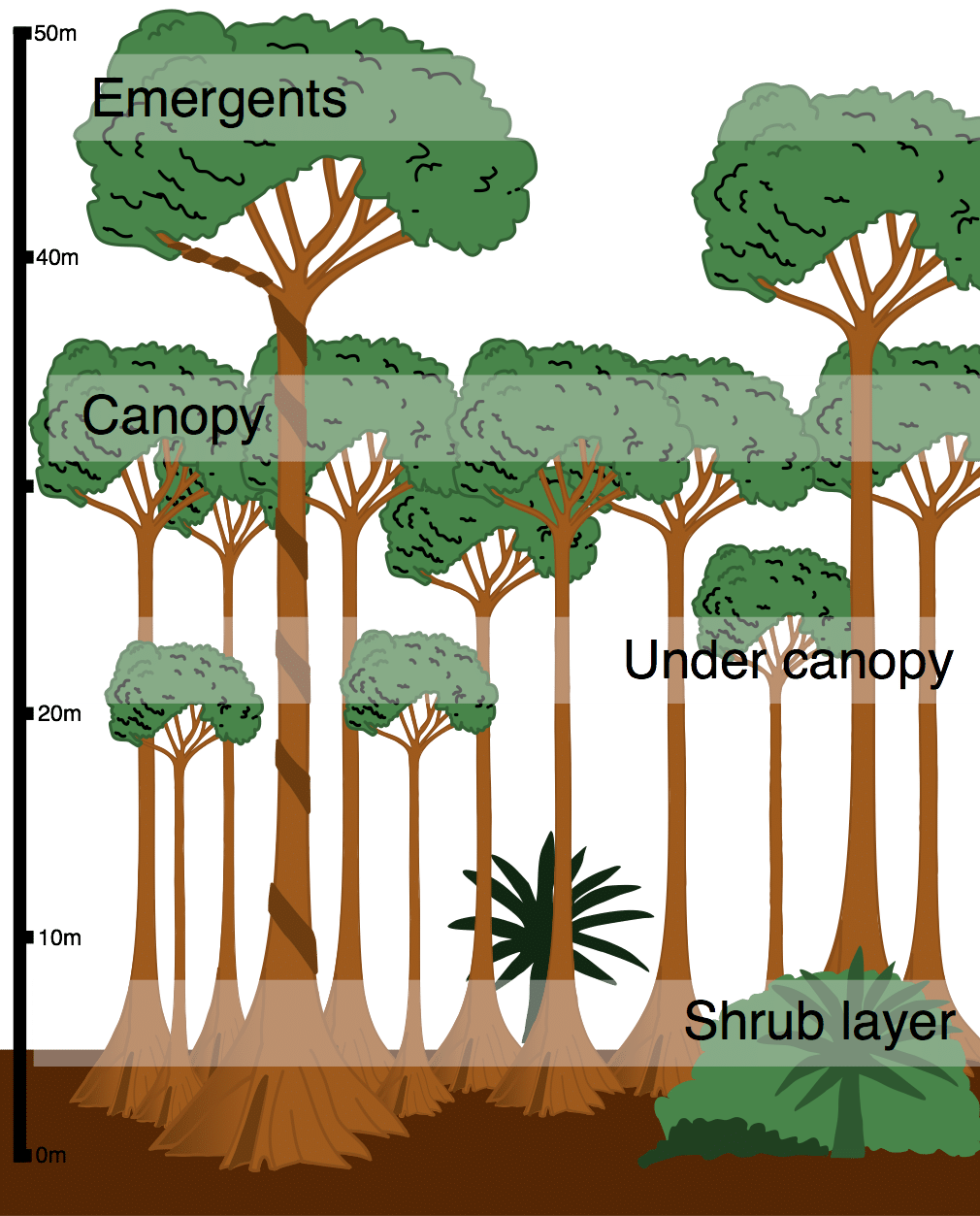
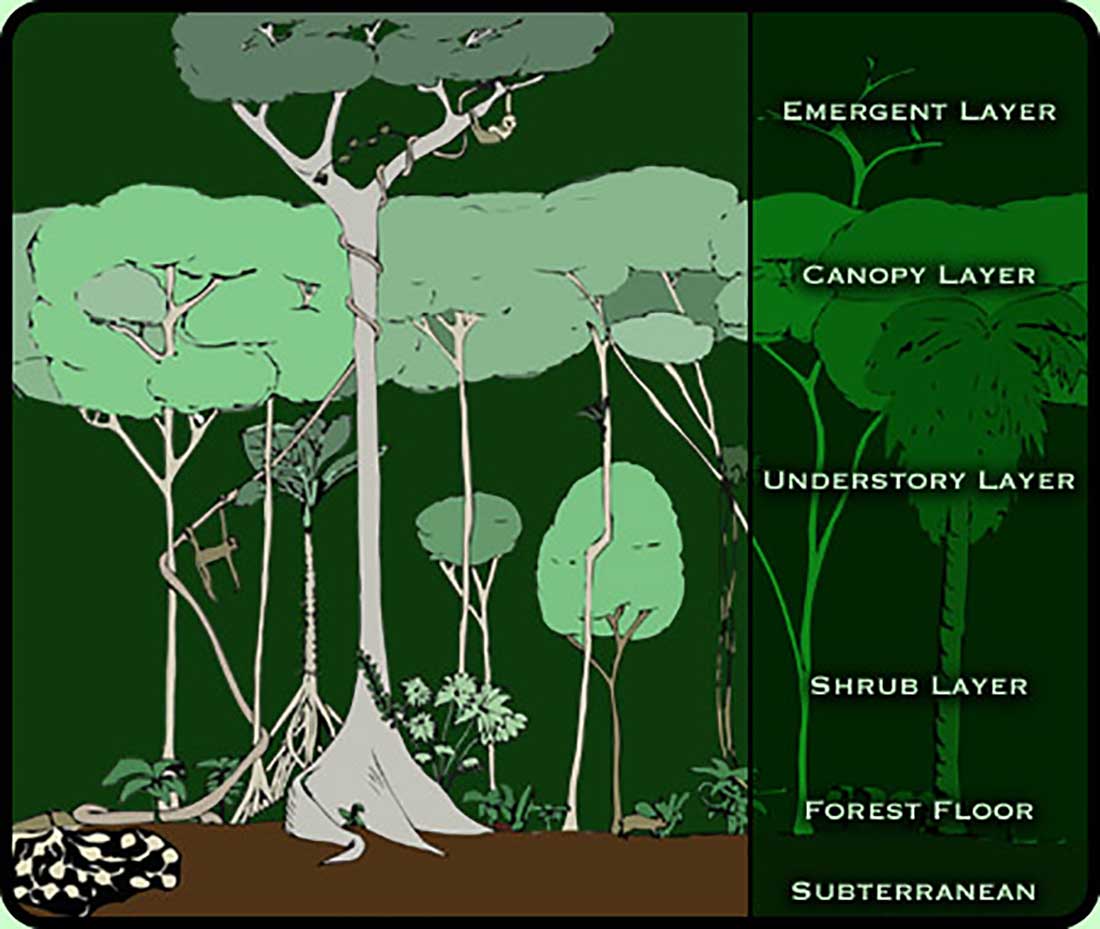
Plants protect themselves from predators using various strategies. Plant Adaptations in the Tropical Rainforest Biome. Most trees in these tropical regions have straight trunks with no branches or leaves until they reach the canopy layer.
Tropical Rainforest Tree Adaptations. Get Sunlight Water Air or Nutrients SWAN Not be eaten Stay attached to a tree or rooted in the ground Reproduce Tropical Rainforest Adaptations The climate of the tropical rainforest is hot and wet. Camouflage mimicry having a limited diet poison reduction of size and stature and changing of habitats with illustrations.
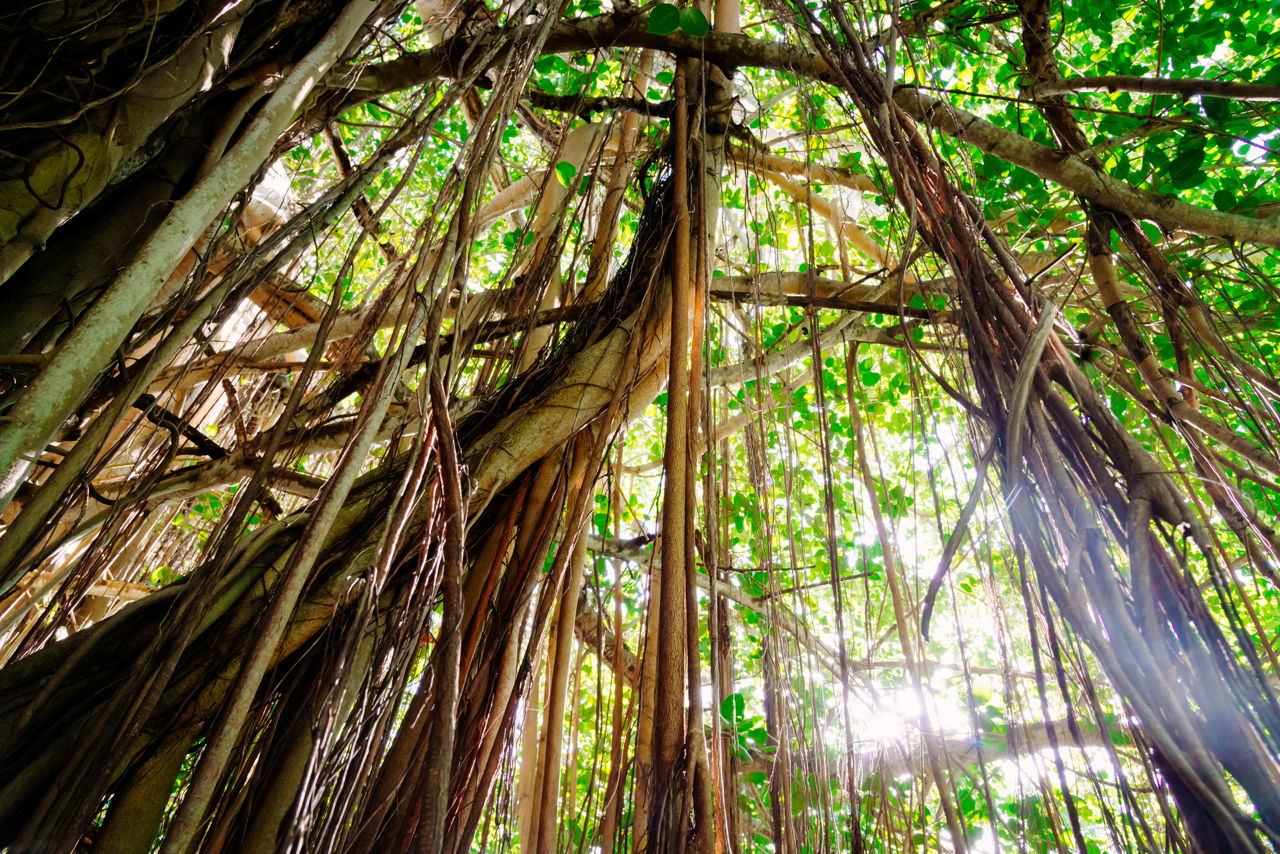
Lianas - these are woody vines that have roots in the ground but climb up the trees to reach the sunlight. The smoothness of the bark may also make it difficult for other plants to grow on their surface. Also some leaves have flexible stems so they can turn toward the sun another adaptation is.
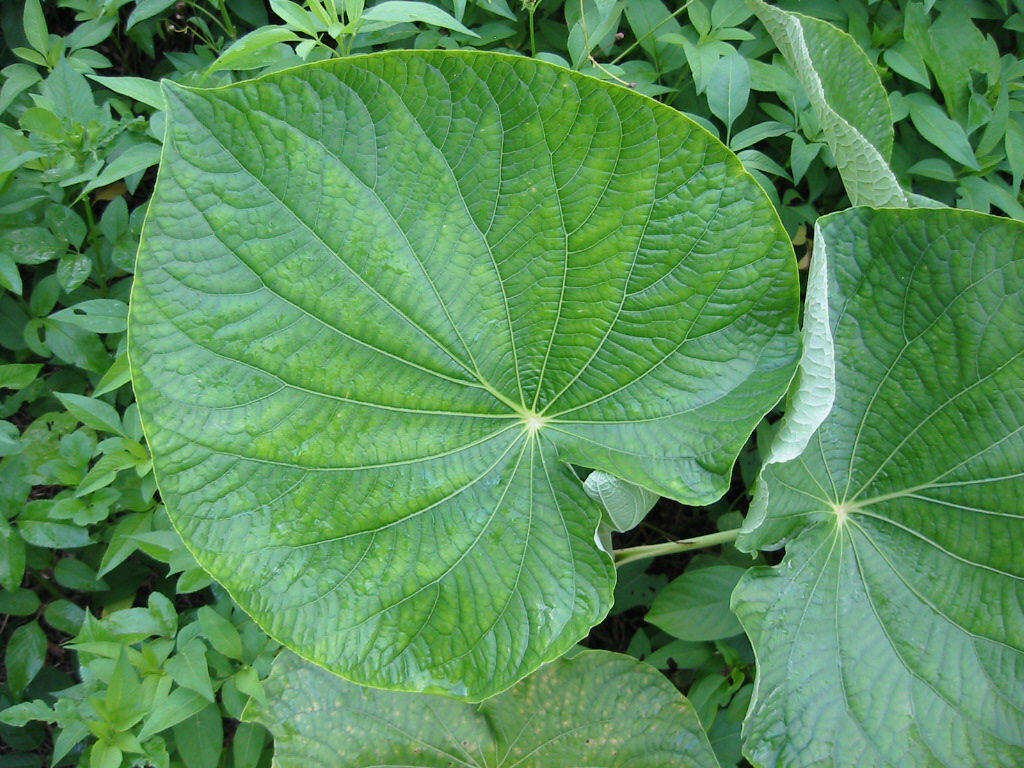
For example some trees such as the kapok grow very tall because of the competition for sunlight. The leaves of forest trees have adapted to cope with exceptionally high rainfall. For example some plants in soil that is low in nutrients have adapted to eat meat while different animals have developed lethal poisons to ward off predators.