Transgenic Animals Examples Ppt
_1602913203_391831-15.jpg)
Transgenic invertebrate species include some.
Transgenic animals examples ppt. Animals against disease and introduction of new genetic traits into herds. Xenotransplanters Transgenic animals that are genetically modified to have organs that can be transplanted into humans. Then common misconceptions will be addressed and the ethics of transgenic animal creation will be discussed.
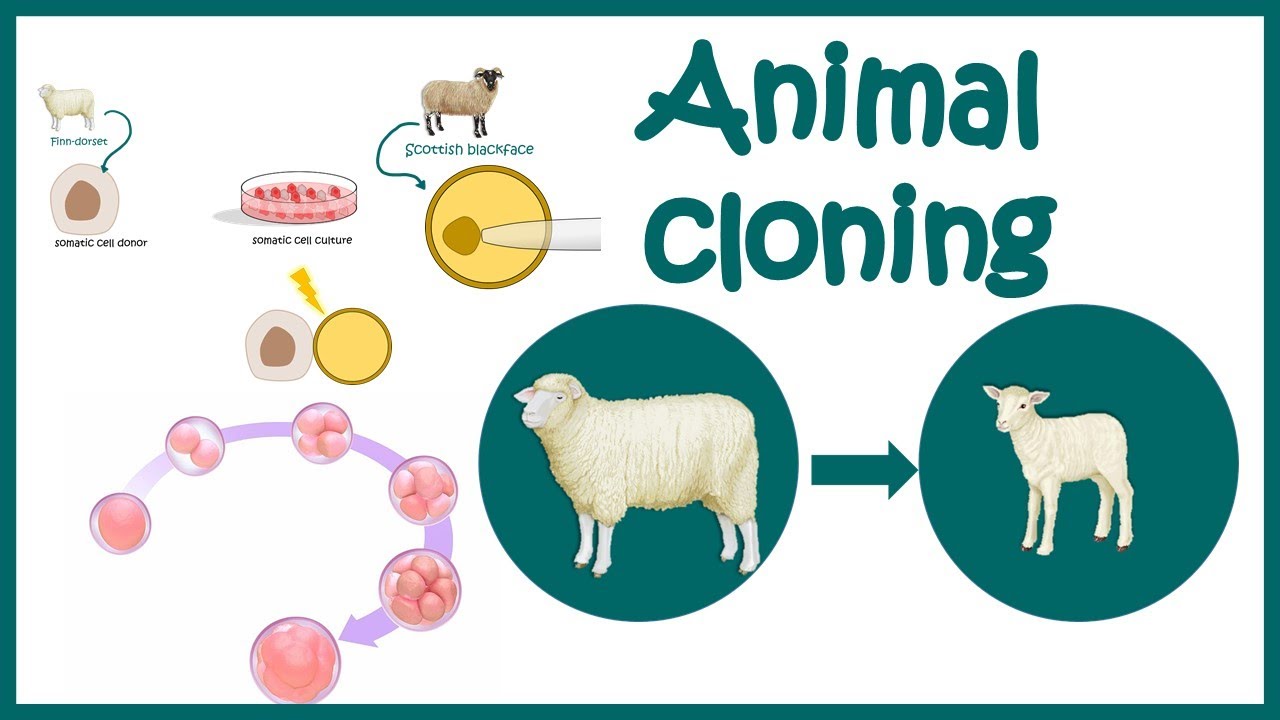
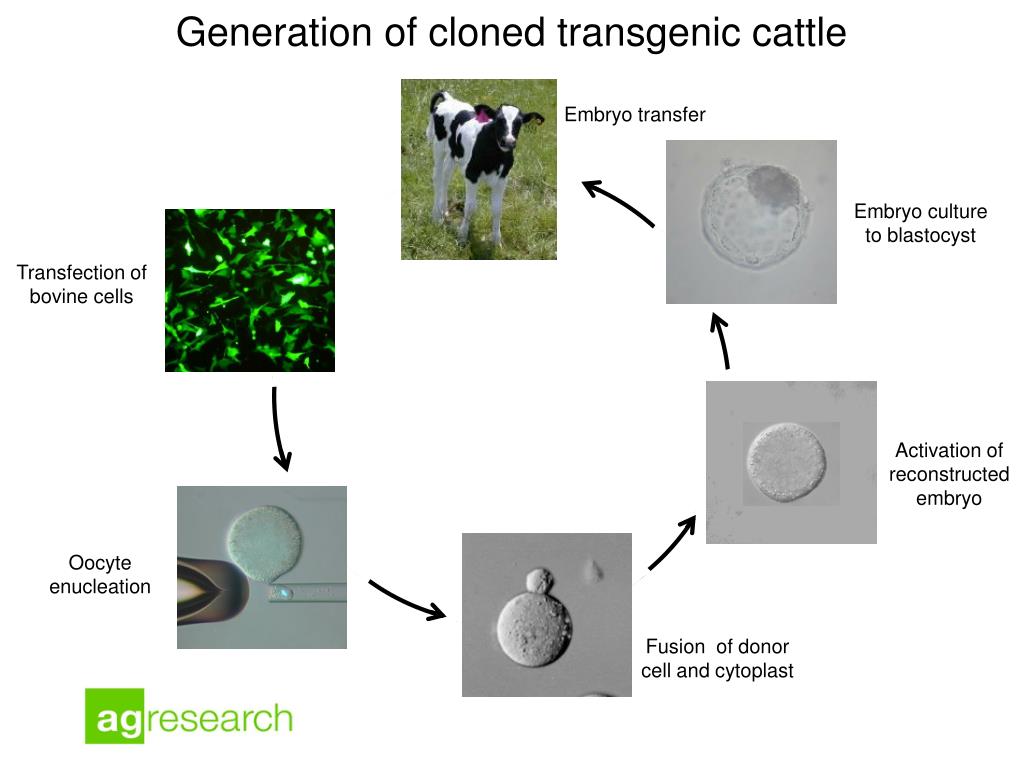
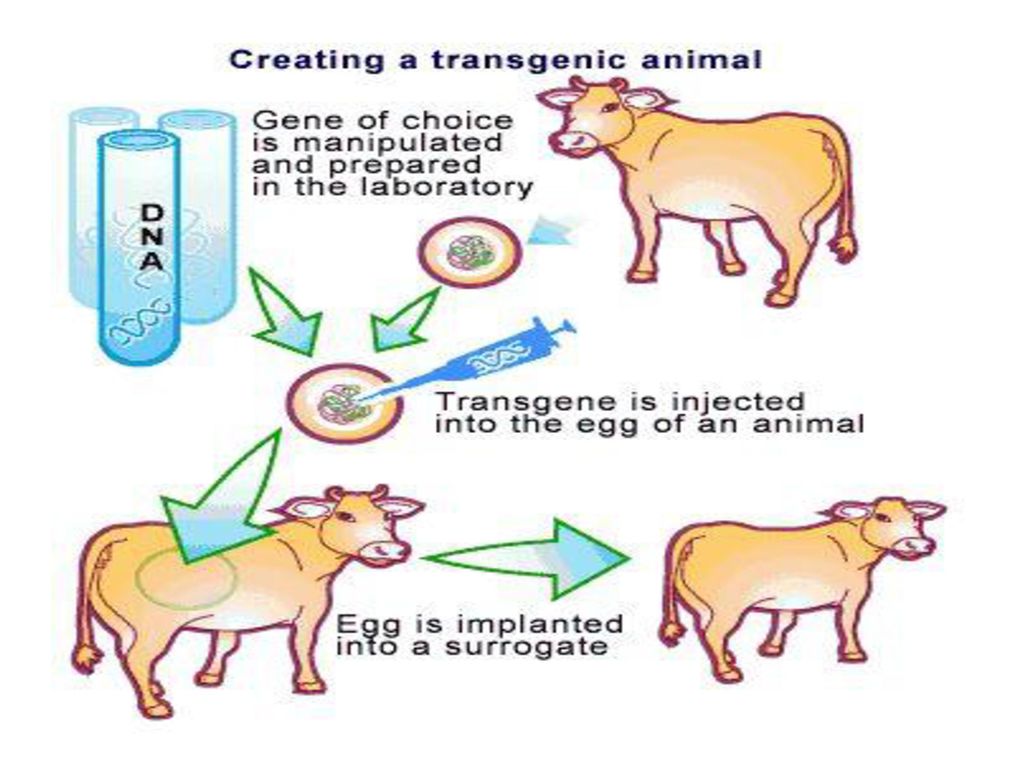
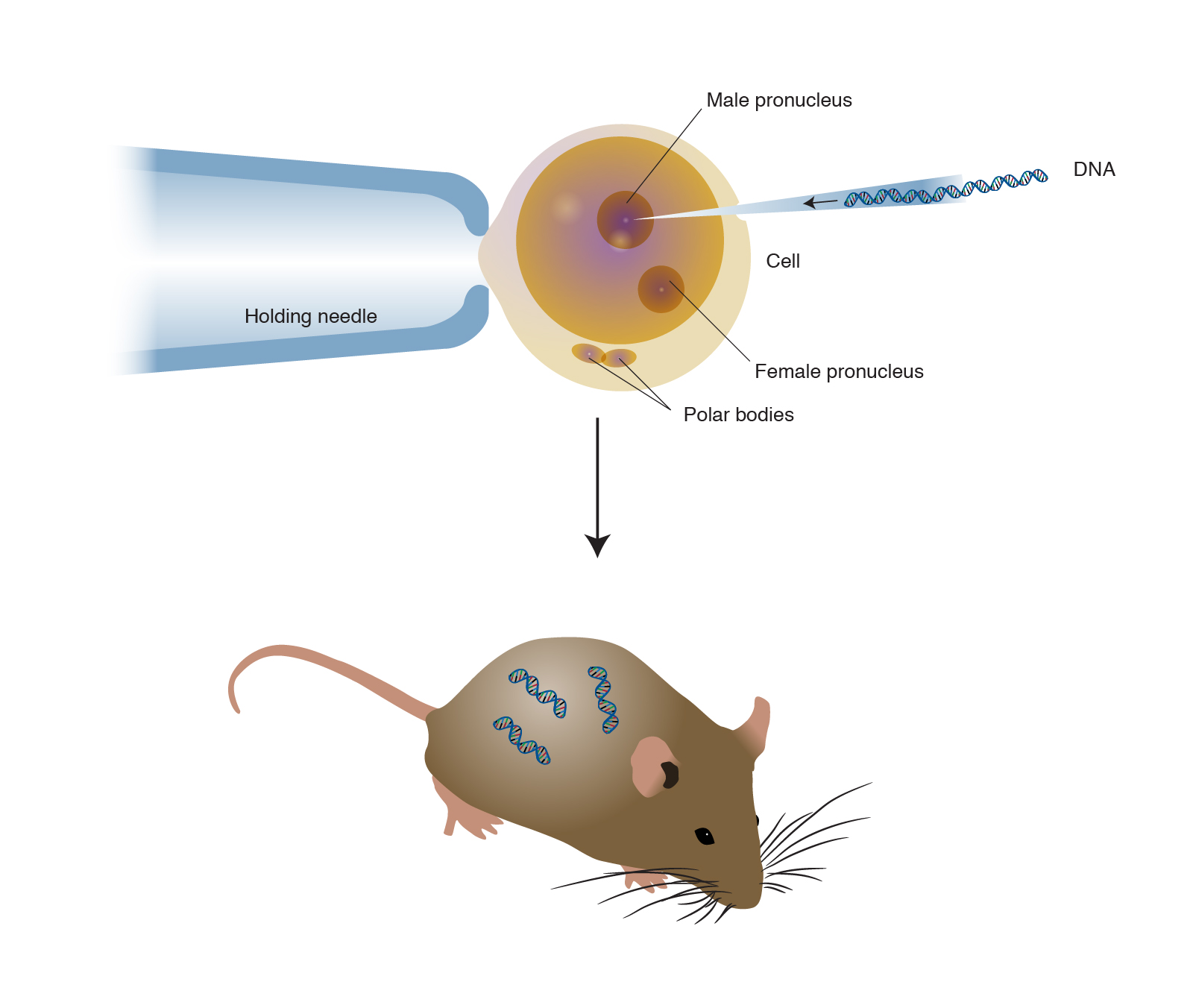
Transgenic animals are created by deliberately inserting a gene into the genome of an animal. Examples of Transgenic Animals. In the interest of educating the public about transgenic animals and determining their effect on society the methods of creating transgenic animals is discussed.
For example Japanese medaka Oryzias latipes and zebrafish Barchydanio rerio have short life cycles 3 months from. The development of transgenic animals has been part of biotechnology research which has been expanding rapidly. 11 These and chronic models for the evaluation of transgenic animals can express HIV-1 proteins.
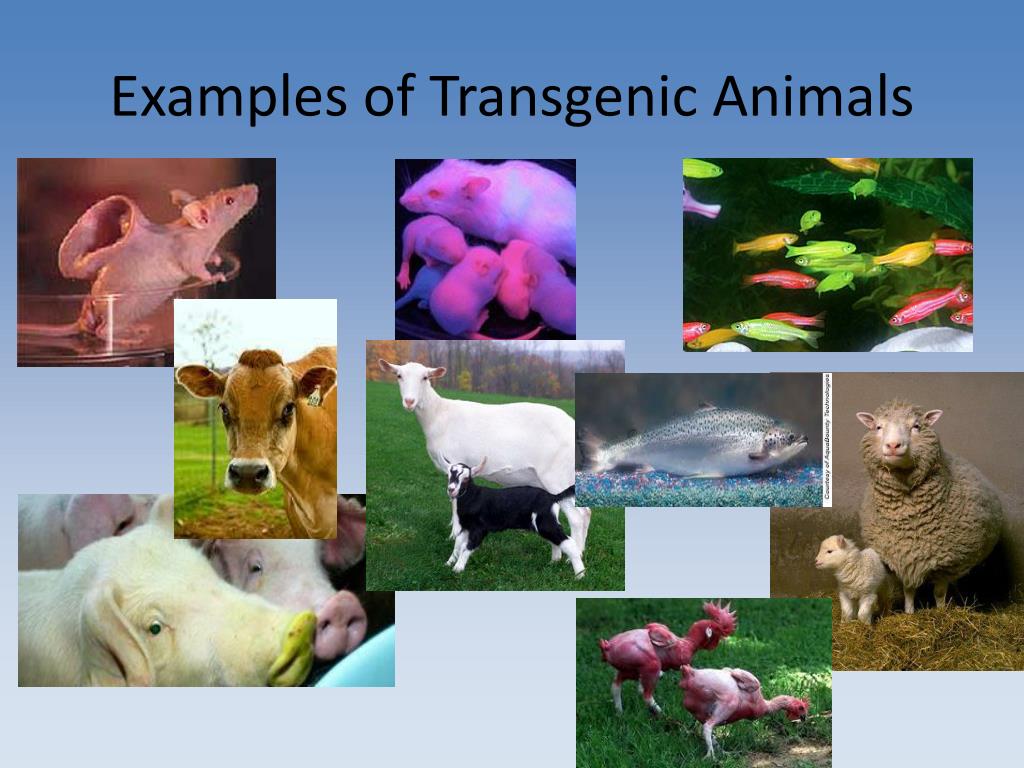
Species transgenic animals examples. Genetically modified salmon was the first transgenic animal for food. Transgenic animals can be used as disease models transpharmers xenotransplanters food sources and other biological models.
In terms of commercially important livestock species work has revolved around specialized non-agricultural purposes such as pharmaceutical production and xenotransplantation and to a lesser extent applied agricultural purposes to improve animal. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. PowerPoint PPT presentation.
Transgenic animals have been produced in a variety of species Table 1. A transgenic animal has been genetically engineered to incorporate a foreign gene. Transgenic models are more precise in comparison to traditional animal models for example the oncomouse with its increased susceptibility to tumor development enables results for carcinogenicity studies to be obtained within a shorter time-frame thus reducing the course of tumor development in experimentally affected animals.
_1602913203_391831-13.jpg)

_1602913203_391831-12.jpg)


_1602913203_391831-14.jpg)
_1602913203_391831-4.jpg)
_1602913203_391831-3.jpg)


_1602913203_391831-2.jpg)