Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

Deep Ocean Animal Adaptations These lessons are part of a deep ocean unit.
Deep ocean animals adaptations. They have streamlined bodies to help them swim fast and gills that suck the oxygen out of the water so they can breathe. 8 12 x 11 blank paper pencil colored pencils ruler or straight edge. In this lesson students consider the diversity of animals in the deep ocean noting similarities and variations in how animals have adapted to their deep ocean environment.
Watch a recording of this video webinar. Food is scarce in much of the deep sea in part because photosynthesis only takes place at the oceans surface where theres sunlight. 4000 m 6000 m and Hadal from 6000 m and below zones Pelagic division includes Mesopelagic 200.
The ocean has three broad habitats. This is often used by animals everywhere for camouflage and protection from predators. The abilities of deep-sea animals to tolerate the pressure and temperature conditions of deep-sea habitats are due to pervasive adaptations at the biochemical level.
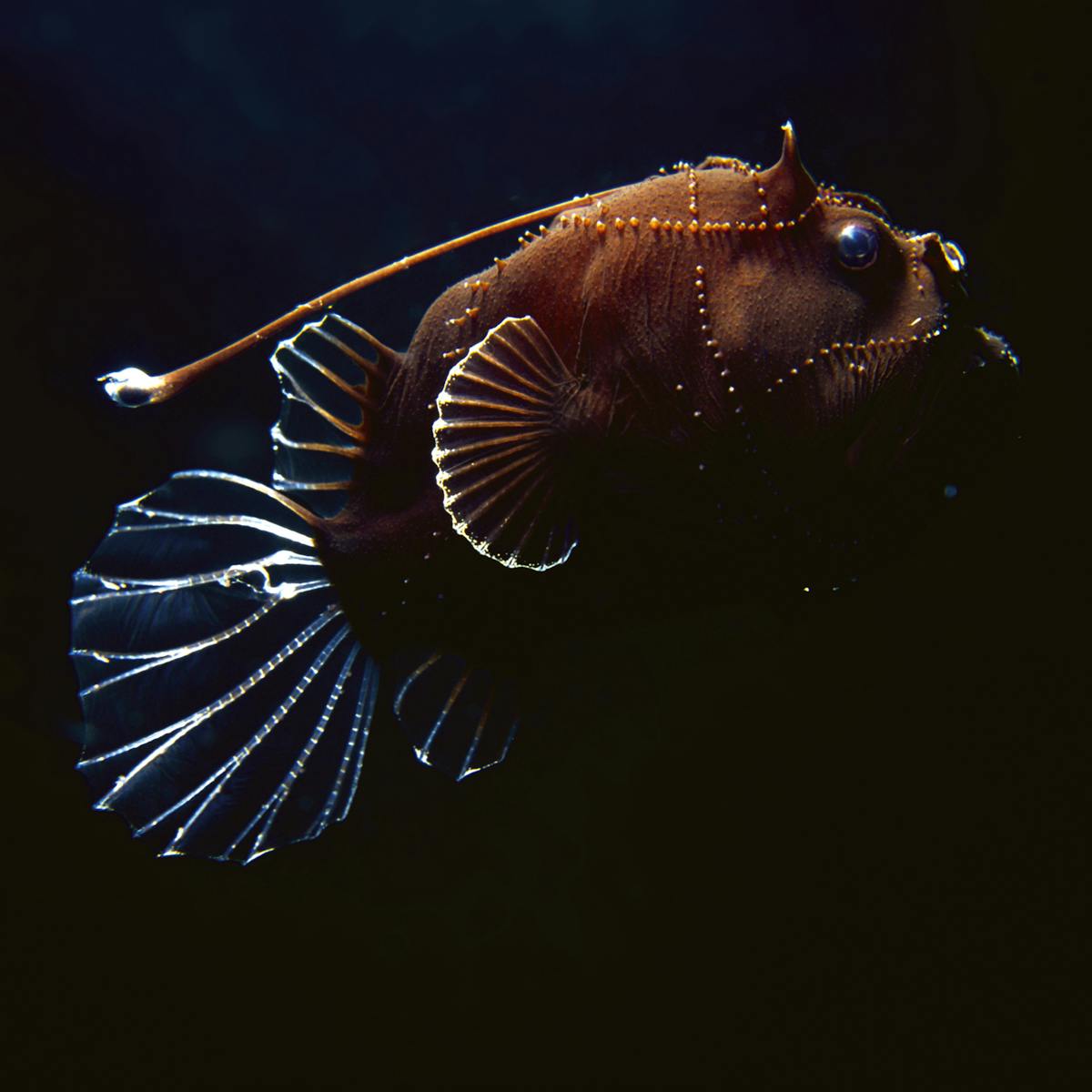
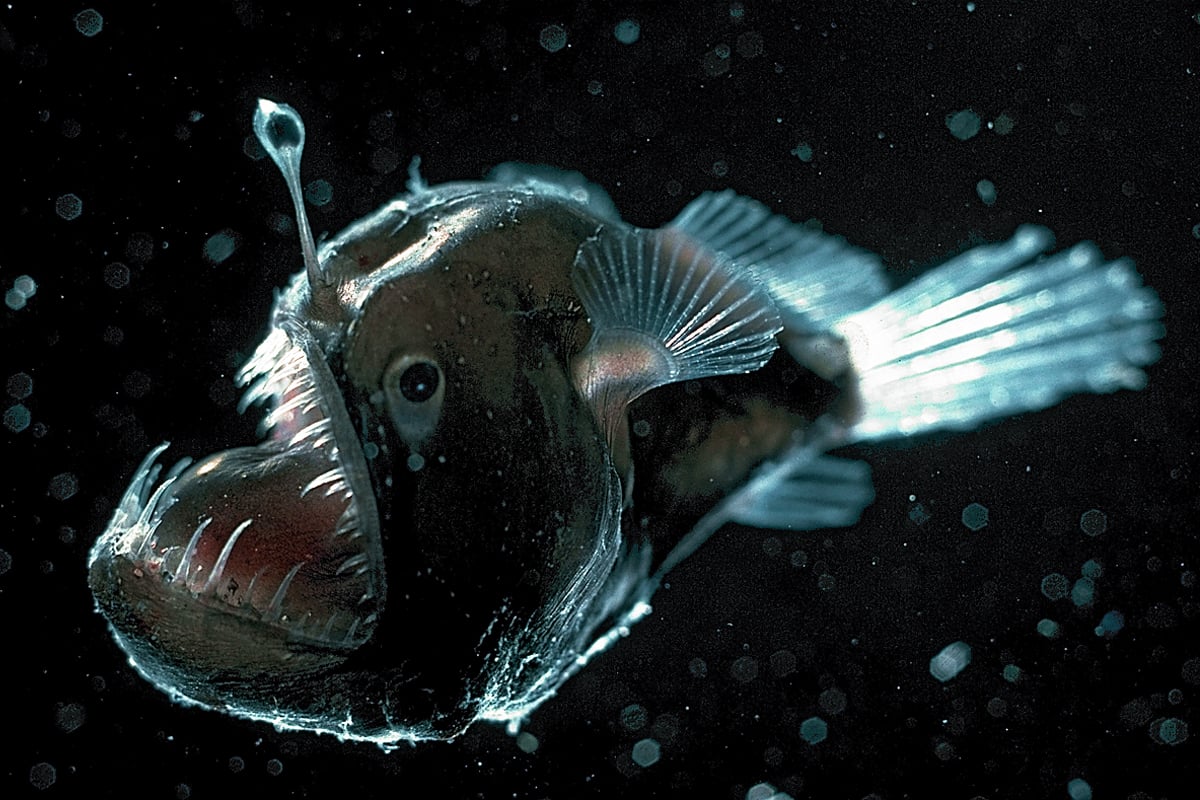
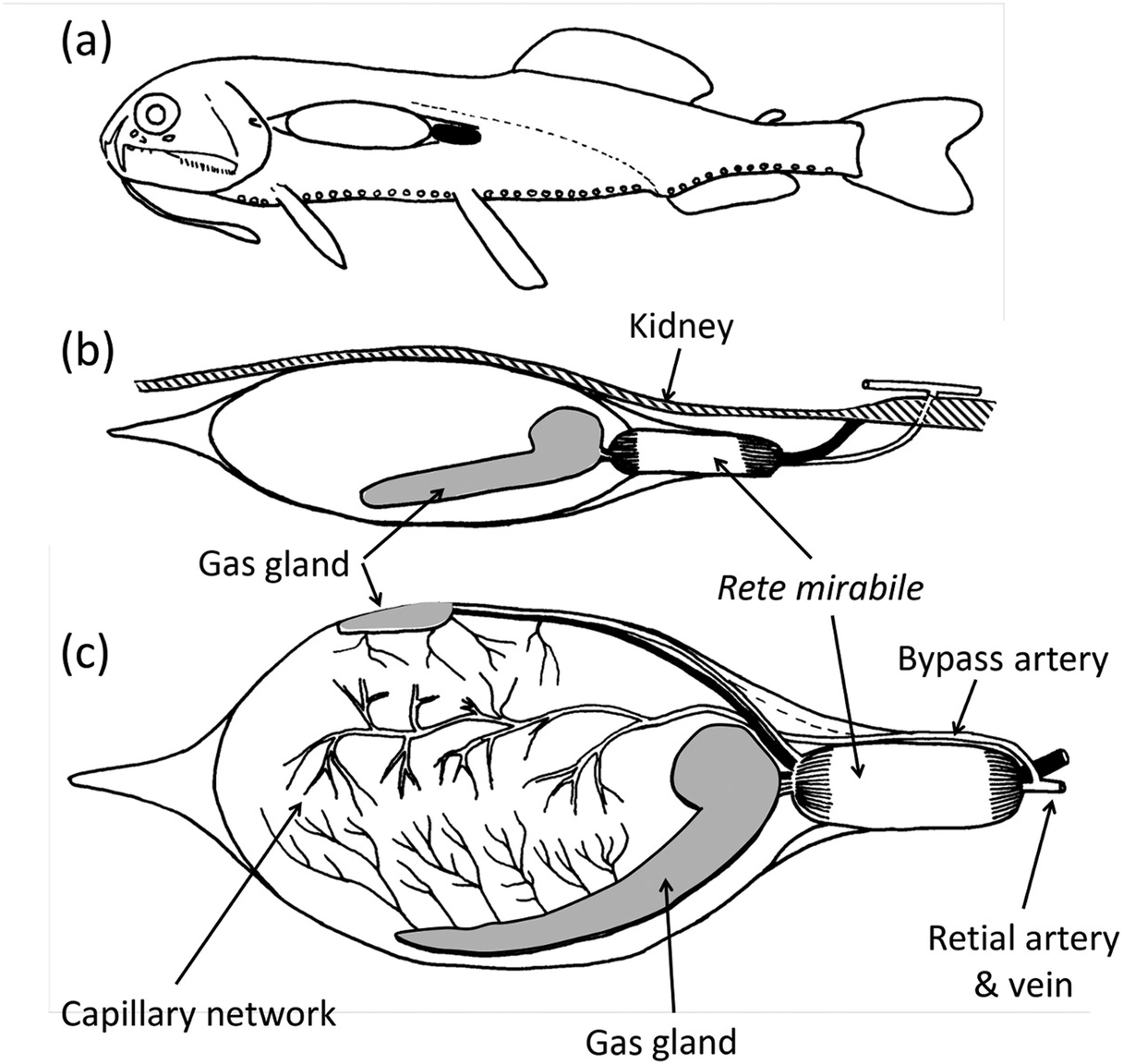
In some other deep-sea fishes eyes are very small as they are of little apparent use and still others are without eyes. These creatures have several adaptations like compressible lungs lung-like swim bladders etc to help them overcome the high water pressure in their deep-water environment. Animals adapt to their environments to help them survive.
The Deep Marine Community Hydrothermal vents. Why are deep sea creatures. First off the deep ocean is dark because sunlight cant penetrate very far into the water.
Seep communities are more dispersed in areas where hydrocarbons particularly methane or other natural gases are percolating up through deep-sea sediments. 5 Other Adaptations of Deep Sea Creatures. Usually lightless sea bottom is referred to as deep sea ie from lower limit of littoral zone 200 metres deep to the ocean floor.