Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

The process of cell catabolism in which cells turn food into usable energy in the form of ATP.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. In this process glucose is broken down in the presence of molecular oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide and much of the energy released is preserved by turning ADP and free phosphate into ATP. Refer to the image below for a quick overview of the process taking place during this respiration.
Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration. ATP for use in energy-requiring activities of the cell.
Cellular respiration can be described as the reverse or opposite of photosynthesis. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. Some organisms such as plants can trap the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis see Chapter 5 and store it in the chemical bonds of carbohydrate molecules.
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP. The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose. Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism.
Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water. The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration.
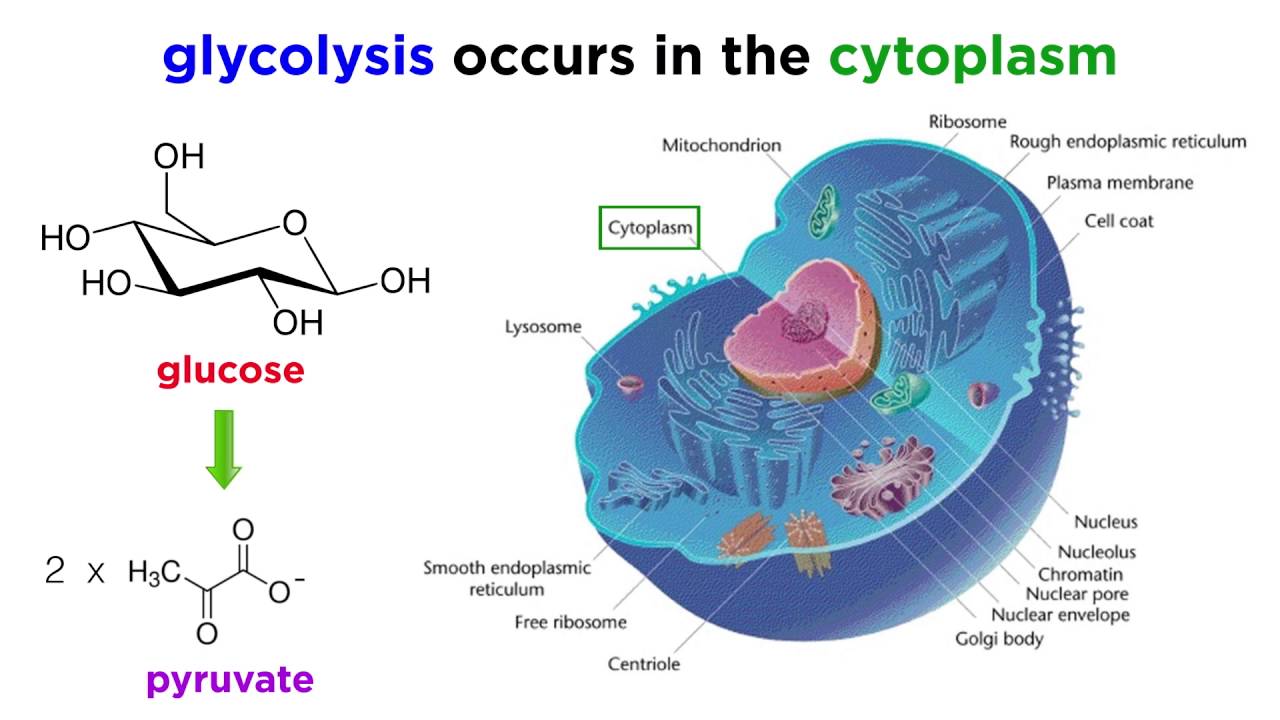
Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. Heterotrophs like humans ingest other living things to obtain glucose.