Cellular Respiration Formula Definition
It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules.
Cellular respiration formula definition. The process involves harvesting biochemical energy from organic molecules especially glucose is converted into ATP adenosine triphosphate. The process takes place in four stages. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in.
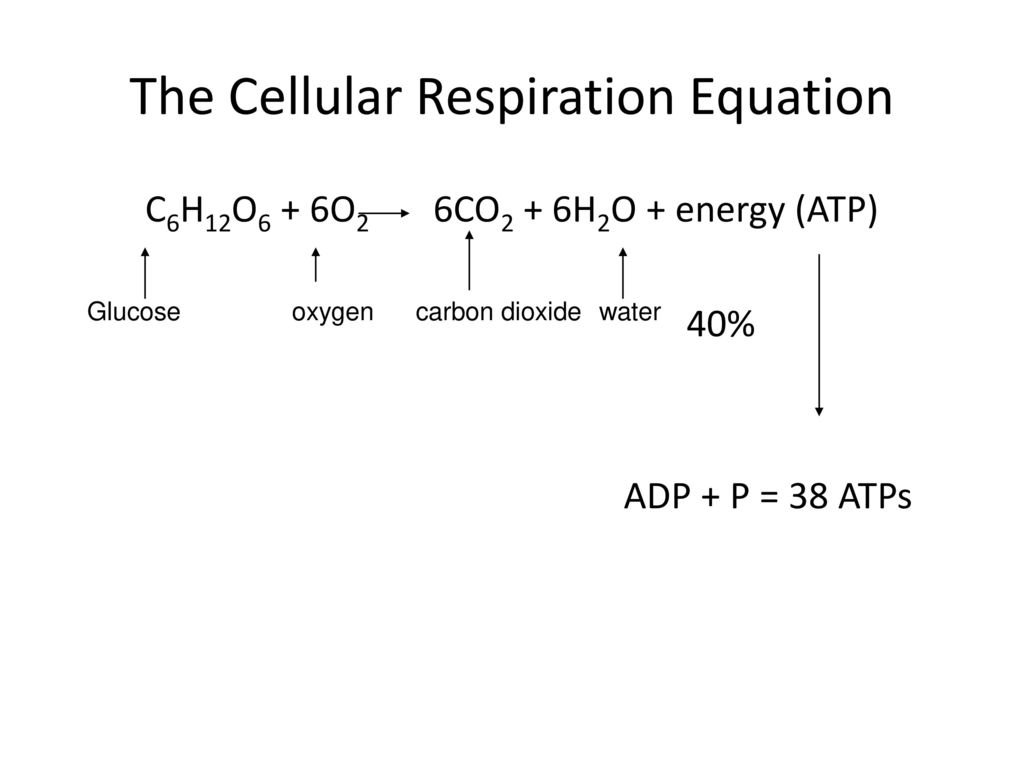
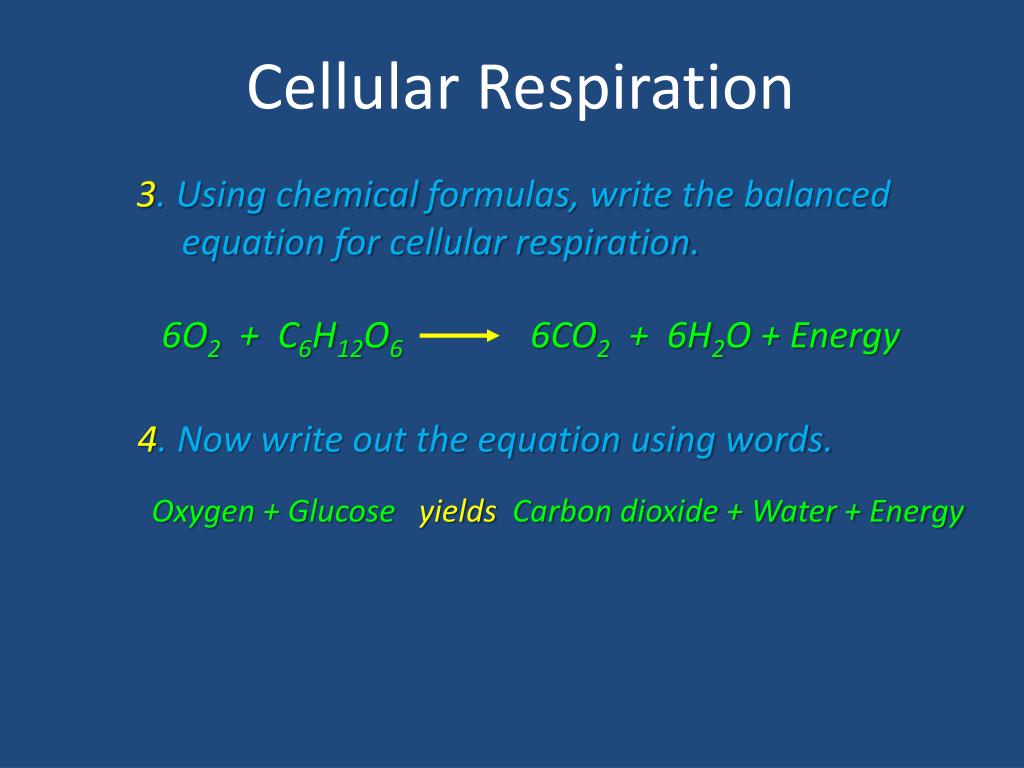
Glucose sugar Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Energy as ATP Aerobic cellular respiration has four stages. Before starting with the equation and the more complicated parts of the subject you can begin with aerobic respiration definition the chemical formula of the cellular respiration etc. Cellular Respiration Formula Definition September 5 2021 Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products.
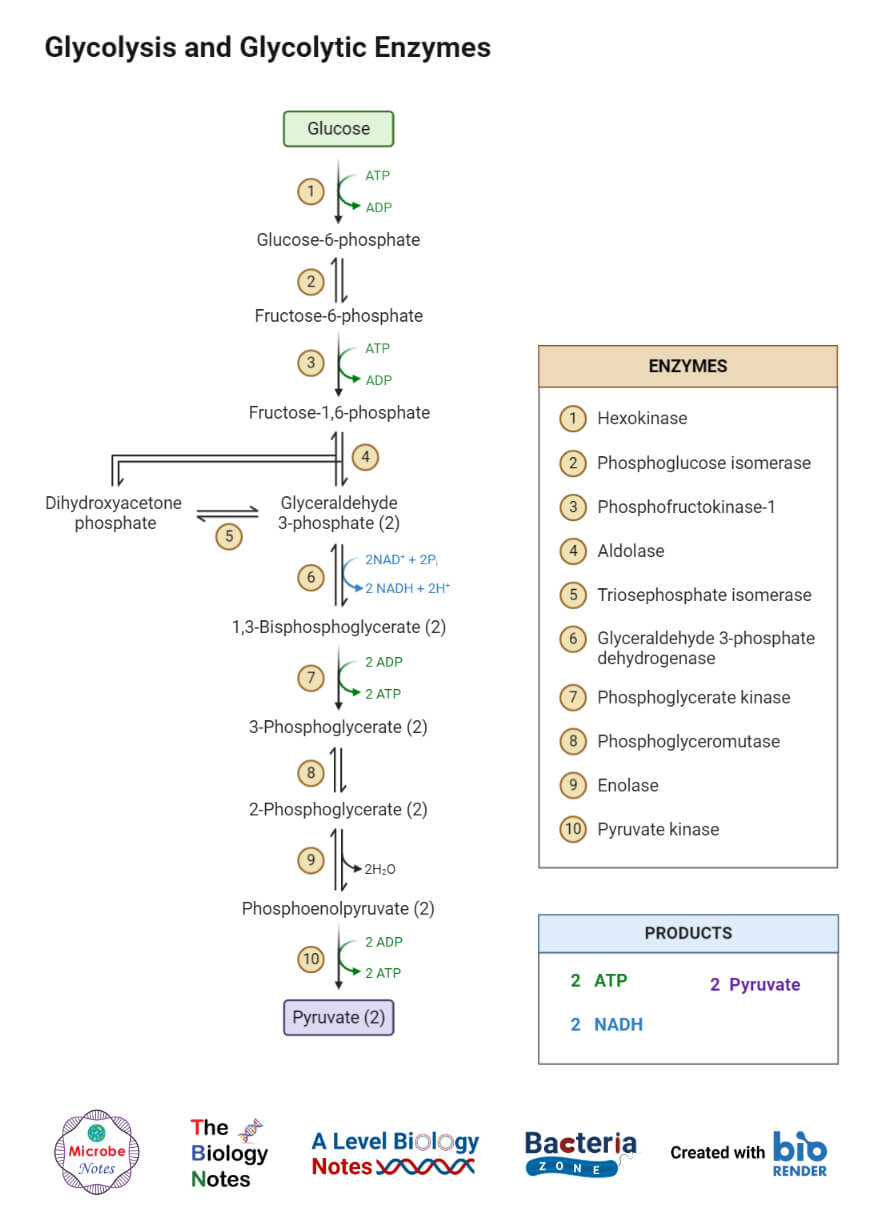
Cellular respiration definition is - any of various energy-yielding oxidative reactions in living matter that typically involve transfer of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide and water as end products. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a metabolic pathway Two types of cellular respiration exist. Also known as the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway it is the first step of cellular respiration.
In photosynthesis what plants need is light energy from the sun carbon dioxide and water. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form. The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates.
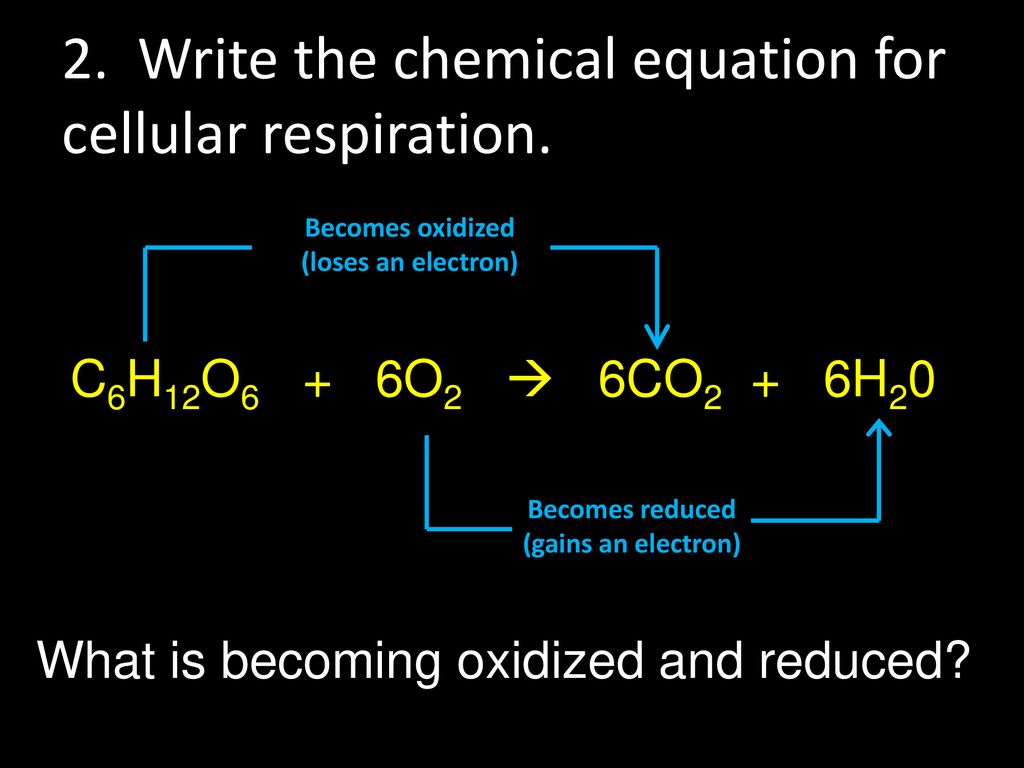
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration an equation an output description and an illustration. Cellular Respiration Definition Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products.
This process breaks down glucose into six carbon dioxide molecules and twelve water molecules. Cellular Respiration Definition. During cellular respiration one glucose molecule combines with six oxygen molecules to produce water carbon dioxide and 38 units of atp.