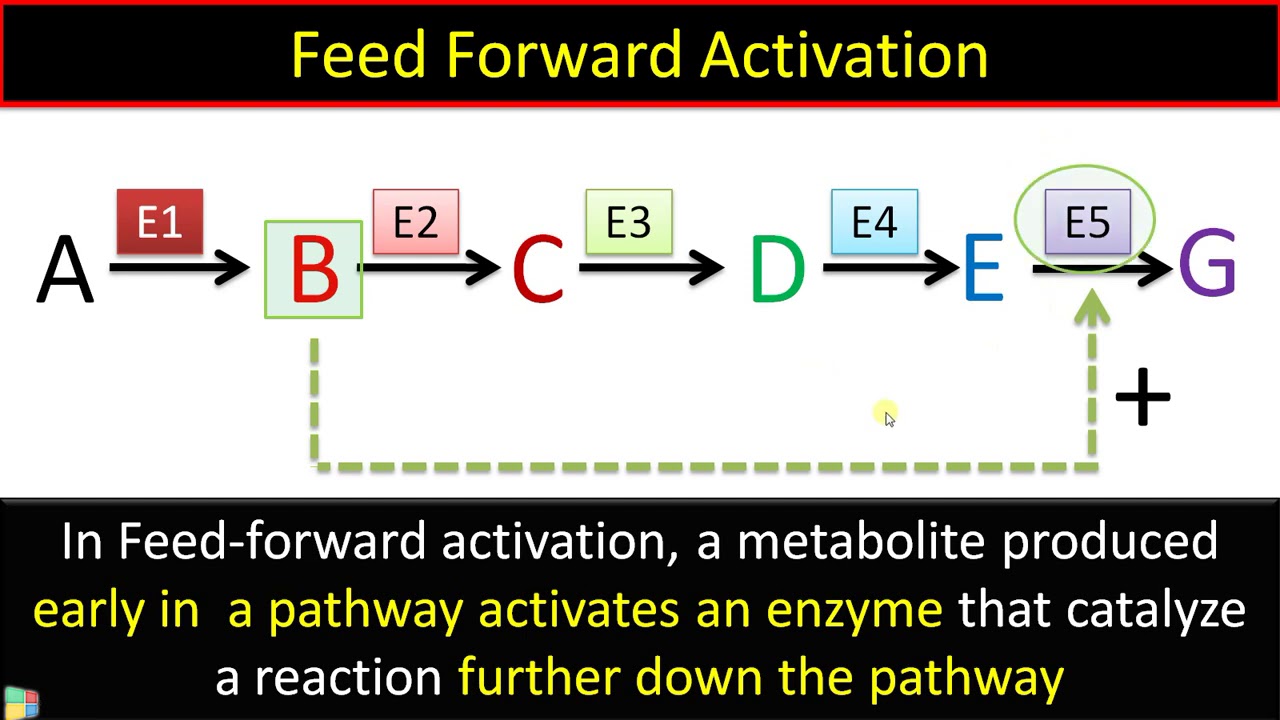
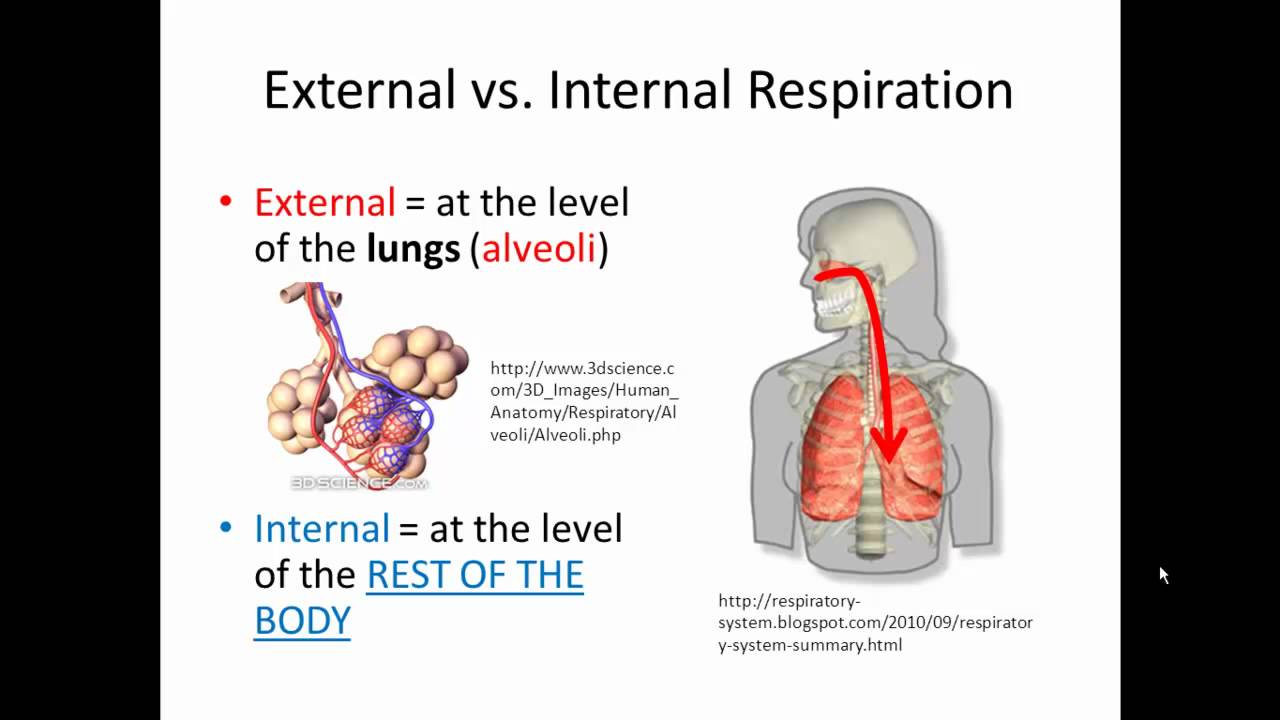
Cellular Respiration Equation Explained

It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water.
Cellular respiration equation explained. Glucose sugar Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Energy as ATP Aerobic cellular respiration has four stages. This process occurs in the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. The overall unbalanced chemical equation for cellular respiration is.
The energy released from the broken down molecules are a result of spontaneous catabolic reactions. Cellular respiration starts off with glycolysis in the cytoplasm the jelly-like fluid that fills a cell. There are two types of electron carriers that are particularly important in cellular respiration.
This type of respiration is common in most of the. Chemical structures of nad and nadh. It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules.
The waste products of this reaction are 6CO2 and 6H2O. Cellular respiration is the process by which food in the form of sugar glucose is transformed into energy within cells. And 6CO2 6H2O 36 ATP are the products.
The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds. Cellular respiration can be summarized as glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water atp energy cellular respiration in plants. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy.
Nutrients are needed for cellular respiration. The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs where it is exchanged for oxygen. At the end of the electron transport chain oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water.