Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

The separation of different parts of the cell with different functions by using membranes is called compartmentalisation providing distinct conditions for different processes.
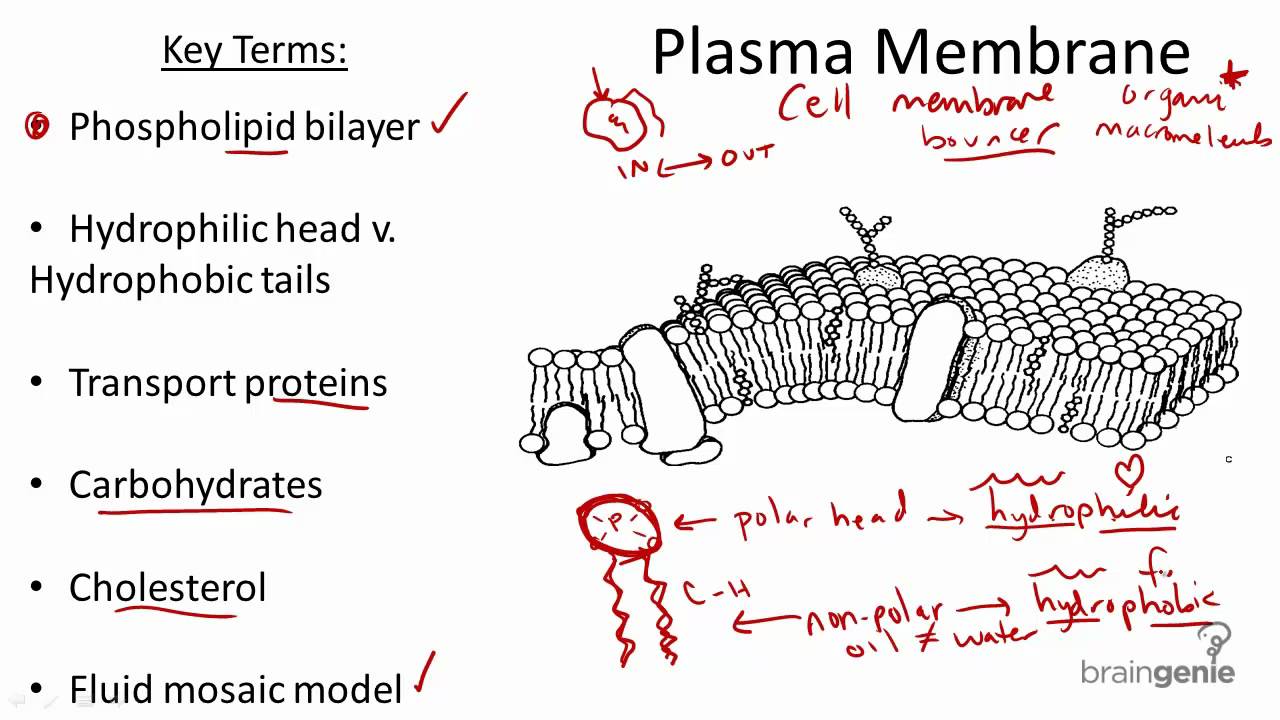
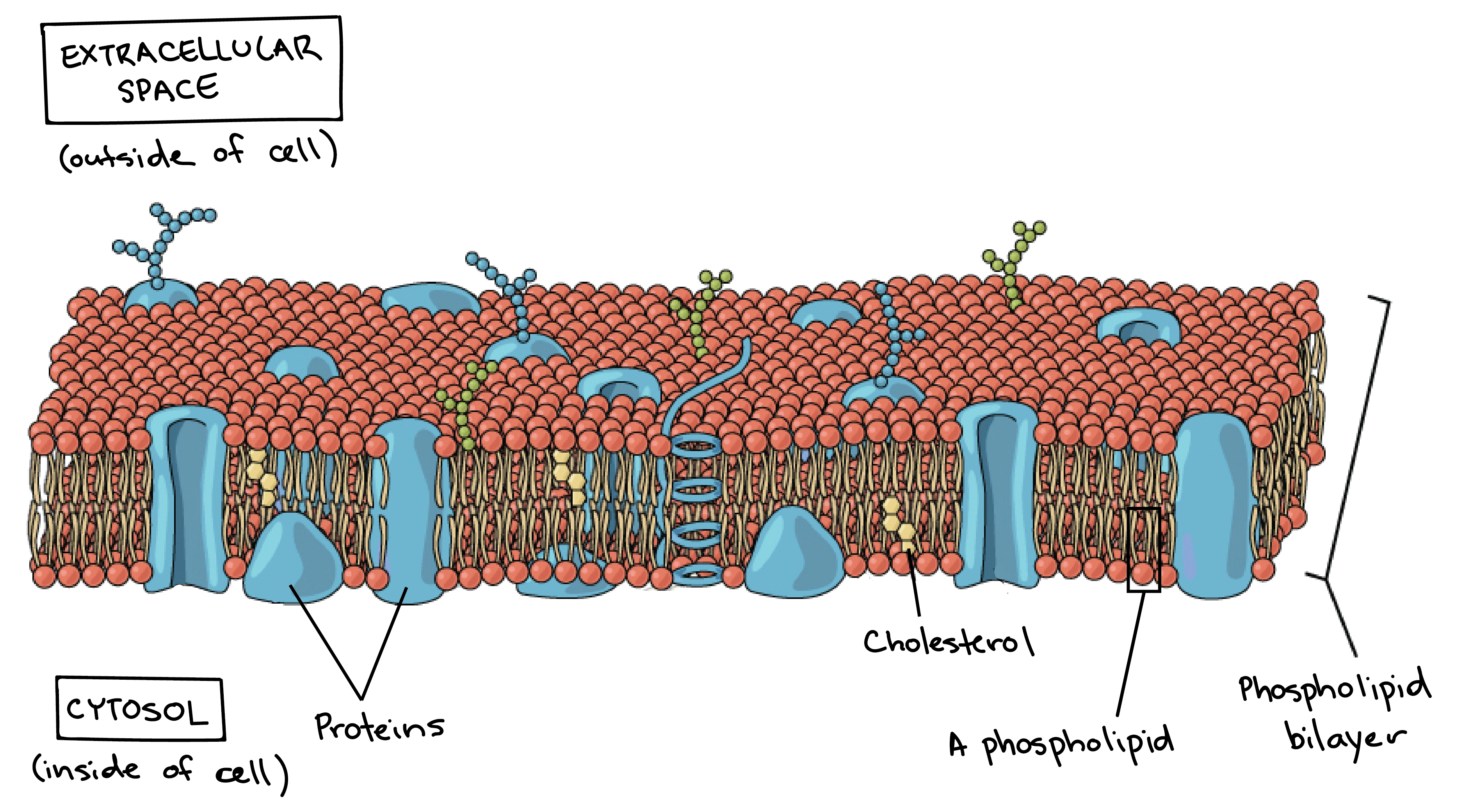
Cell membrane structure and function a level. -A double membrane sac which pinches off the end of organelles such as the RER or Golgi Apparatus and fuses with other membranes such as the RER Golgi or Plasma Membrane Function of Vesicles -Transport proteins and other substances between organelles and the outside of the cell. Many membranes within the cell help to make different compartments for different chemical reactions to take place. This is a thin flexible layer round the outside of all cells made of phospholipids and proteins.
This structure can even be called the inner membrane to distinguish it from the outer membrane present in gram-negative bacteria. Membranes formed from phospholipid bilayers help to compartmentalise different regions within the cell as well as forming the cell surface membrane Exam Tip An example of a membrane-bound organelle is the lysosome found in animal cells each containing many hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many different kinds of biomolecule. The fundamental structure of the plasma membrane.
1 Isolate cells contents from outside environment 2 Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3 Communicate with other cells Note. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures. All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes and this characteristic best portrayed by the Fluid Mosaic ModelAccording to this model which was postulated by Singer and Nicolson during the 1970s plasma membranes are composed of lipids proteins and carbohydrates that are arranged in a mosaic-like manner.
Every cell has a lipid and protein layer called cell membrane or cytoplasmic or plasma which defines its boundaries and regulates molecular exchanges with the external environment. Organisms are composed of cells and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. Membranes are selectively permeable so are effective barriers in controlling what goes in and out of cells.
Functions of membrane systems and organelles. These structures are called Organelles. The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cells cytoplasm.
Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals. Because the membrane is fluid and because of the mosaic arrangement of the protein molecules the structure of the membrane. In plant cells the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm.